现在懒死了,八个月没有更新博客了,今天在处理一个业务网卡丢包的问题,监控查看丢包源是在机器进方向丢包的,通过ethtool查看计数器的值和ifconfig的dropped值哪个是一样的(也可以相近的毕竟也有个别其他情况丢的包,比如crc等。),判断丢包类型,通过rx_out_of_buffer计数器确认丢包类型,表面意思看起来和buffer有关系,但不确定具体的解释,通过网上搜索,确认这个计数器的解释,最终通过修改ring buffer降低了业务的丢包率。修改方法比较简单,如下:
查看当前设置:
ethtool -g eth0
Ring parameters for eth0:
Pre-set maximums:
RX: 8192
RX Mini: 0
RX Jumbo: 0
TX: 8192
Current hardware settings:
RX: 8192
RX Mini: 0
RX Jumbo: 0
TX: 8192
修改设置:
ethtool -G eth0 rx 8192
ethtool -G eth0 tx 8192
ethtool -g eth0
Ring parameters for eth0:
Pre-set maximums:
RX: 8192
RX Mini: 0
RX Jumbo: 0
TX: 8192
Current hardware settings:
RX: 8192
RX Mini: 0
RX Jumbo: 0
TX: 8192
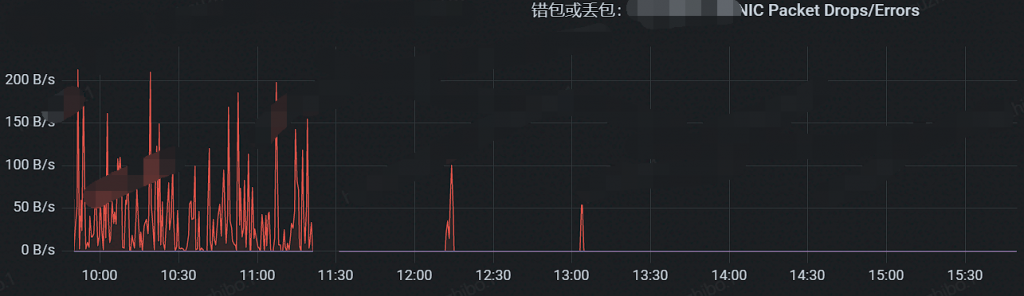
中午11:30左右修改前后丢包对比
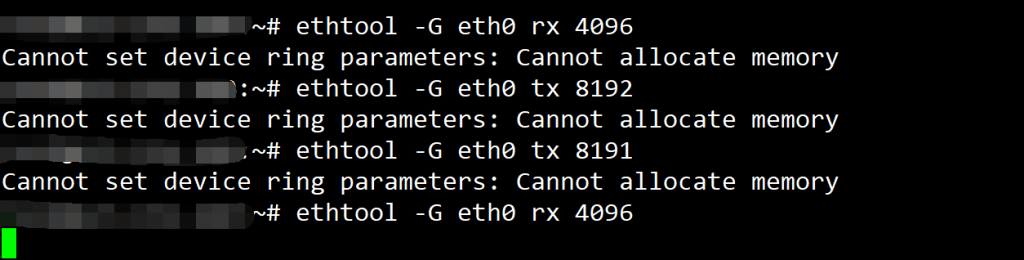
在修改的过程中遇到了一个莫名其妙的bug,导致我尝试在第四次修改的时候服务器自己重启了,在这没有去排查具体重启的原因,重启之后就可以正常顺利的修改了。有重要业务的同学,建议停服再操作,我当时报错的记录如下:
由于所搜的历程比较麻烦,所以做个记录分享下,Mellanox mlx5 ethtool计数器的解释,摘自Mellanox 官网。原链接:https://support.mellanox.com/s/article/understanding-mlx5-ethtool-counters
Understanding mlx5 ethtool Counters
Description:
This post shows the list of ethtool counters applicable for ConnectX-4 and above (mlx5 driver). All counters listed here are available via ethtool starting with MLNX_OFED 4.0.
Note: The post also provides a reference to ConnectX-3/ConnectX-3 Pro counters that co-exist for the mlx4 driver (see notes below).
References
- MLNX_OFED User Manual
- Netstat tool
Release Notes
This document was updated to match Linux kernel 4.20
Counters Overview
There are several counter groups, depends where the counter is being counted. In addition, each group of counters may have different counter types.
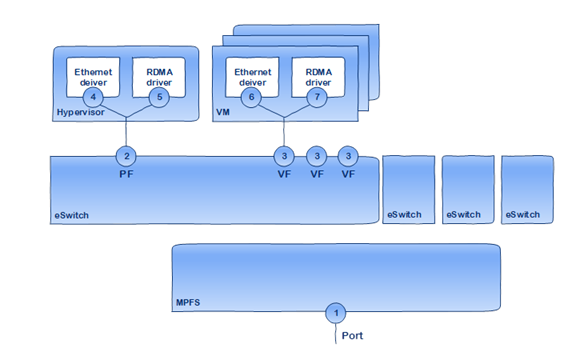
Counter Groups
- Ring – software ring counters
- Software Port – An aggregation of software ring counters.
- vPort counters – traffic counters and drops due to steering or no buffers. May indicate on NIC issues. These counters include Ethernet traffic counters (including Raw Ethernet) and RDMA/RoCE traffic counters.
- Physical port counters – the physical port connecting NIC to the network. May indicate on NIC issues or link or network issue. This measuring point holds information on standardized counters like IEEE 802.3, RFC2863, RFC 2819, RFC 3635 and additional counters like flow control, FEC and more. Physical port counters are not exposed to virtual machines.
- Priority Port Counters – A set of the physical port counters, per priory per port.
Counter Types
Counters are divided to three Types
- Traffic Informative Counters – counters which counts traffic. These counters can be used for load estimation of for general debug.
- Traffic Acceleration Counters – counters which counts traffic which was accelerated by Mellanox driver or by hardware. The counters are an additional layer to the informative counter set and the same traffic is counted in both informative and acceleration counters. Acceleration counters are marked with [A].
- Error Counters – Increment of these counters might indicate a problem. Each of these counter has an explanation and correction action.
Statistic can be fetched via the ip link or ethtool commands. ethtool provides more detailed information.
ip –s link show <if-name>
ethtool -S <if-name>
Acceleration Mechanism
The following acceleration mechanisms have dedicated counters:
- TSO (TCP Segmentation Offload) – increasing outbound throughput and reducing CPU utilization by allowing the kernel to buffer multiple packets in a single large buffer. The NIC split the buffer into packet and transmits it
- LRO (Large Receive Offload) – increasing inbound throughput and reducing CPU utilization by aggregation of o multiple incoming packet of a single stream to a single buffer
- CHECKSUM (Checksum) – calculation of TCP checksum (by the NIC). The following CSUM offload are available (refer to skbuff.h for detailed explanation)
- CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY
- CHECKSUM_NONE – no CSUM acceleration was used
- CHECKSUM_COMPLETE – Device provided CSUM on the entire packet
- CHECKSUM_PARTIAL – Device provided CSUM
- CQE Compress – compression of Completion Queue Events (CQE) used for sparing bandwidth on PCIe and hence achieve better performance.
Counters Description
Ring / Software Port Counters
The following counters are available per ring or Software port.
These counters provide information on the amount of traffic that was accelerated by the NIC. The counters are counting the accelerated traffic in addition to the standard counters which counts it (i.e. accelerated traffic is counted twice).
The counter names in the table below refers to both ring and port counters. the notation for ring counters includes the [i] index without the braces. the notation for port counters doesn’t include the [i]. a counter name rx[i]_packets will be printed as rx0_packets for ring 0 and rx_packets for the software port
Ring / Software Port Counter Table
| Counter | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| rx[i]_packets | The number of packets received on ring i.ConnectX-3 naming : rx[i]_packets | Informative |
| rx[i]_bytes | The number of bytes received on ring i.ConnectX-3 naming : rx[i]_bytes | Informative |
| tx[i]_packets | The number of packets transmitted on ring i.ConnectX-3 naming : tx[i]_packets | Informative |
| tx[i]_bytes | The number of bytes transmitted on ring i.ConnectX-3 naming : tx[i]_bytes | Informative |
| tx[i]_tso_packets | The number of TSO packets transmitted on ring i [A]. | Acceleration |
| tx[i]_tso_bytes | The number of TSO bytes transmitted on ring i [A]. | Acceleration |
| tx[i]_tso_inner_packets | The number of TSO packets which are indicated to be carry internal encapsulation transmitted on ring i [A] | Acceleration |
| tx[i]_tso_inner_bytes | The number of TSO bytes which are indicated to be carry internal encapsulation transmitted on ring i [A]. | Acceleration |
| rx[i]_lro_packets | The number of LRO packets received on ring i [A]. | Acceleration |
| rx[i]_lro_bytes | The number of LRO bytes received on ring i [A]. | Acceleration |
| rx[i]_csum_unnecessary | Packets received with a CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY on ring i [A]. | Acceleration |
| rx[i]_csum_none | Packets received with CHECKSUM_NONE on ring i [A]. | Acceleration |
| rx[i]_csum_complete | Packets received with a CHECKSUM_COMPLETE on ring i [A]. | Acceleration |
| rx[i]_csum_unnecessary_inner | Packets received with inner encapsulation with a CHECK_SUM UNNECESSARY on ring i [A]. | Acceleration |
| tx[i]_csum_partial | Packets transmitted with a CHECKSUM_PARTIAL on ring i [A]. | Acceleration |
| tx[i]_csum_partial_inner | Packets transmitted with inner encapsulation with a CHECKSUM_PARTIAL on ring i [A]. | Acceleration |
| tx[i]_csum_none | Packets transmitted with no hardware checksum acceleration on ring i. | Informative |
| tx[i]_stoppedtx_queue_stopped (1) | Events where SQ was full on ring i. If this counter is increased, check the amount of buffers allocated for transmission. | Error |
| tx[i]_waketx_queue_wake (1) | Events where SQ was full and has become not full on ring i. | Error |
| tx[i]_droppedtx_queue_dropped (1) | Packets transmitted that were dropped due to DMA mapping failure on ring i. If this counter is increased, check the amount of buffers allocated for transmission. | Error |
| rx[i]_wqe_err | The number of wrong opcodes received on ring i. | Error |
| tx[i]_nop | The number of no WQEs (empty WQEs) inserted to the SQ (related to ring i) due to the reach of the end of the cyclic buffer. When reaching near to the end of cyclic buffer the driver may add those empty WQEs to avoid handling a state the a WQE start in the end of the queue and ends in the beginning of the queue. This is a normal condition. | Informative |
| rx[i]_mpwqe_frag | The number of WQEs that failed to allocate compound page and hence fragmented MPWQE’s (Multi Packet WQEs) were used on ring i. If this counter raise, it may suggest that there is no enough memory for large pages, the driver allocated fragmented pages. This is not abnormal condition. | Informative |
| rx[i]_mpwqe_filler_cqes | The number of filler CQEs events that where issued on ring i.berfore kernel 4.19 name was rx[i]_mpwqe_filler | Informative |
| rx[i]_cqe_compress_blks | The number of receive blocks with CQE compression on ring i [A]. | Acceleration |
| rx[i]_cqe_compress_pkts | The number of receive packets with CQE compression on ring i [A]. | Acceleration |
| rx[i]_cache_reuse | The number of events of successful reuse of a page from a driver’s internal page cache – supported from Kernel 4.9 | Acceleration |
| rx[i]_cache_full | The number of events of full internal page cache where driver can’t put a page back to the cache for recycling (page will be freed) – supported from Kernel 4.9 | Acceleration |
| rx[i]_cache_empty | The number of events where cache was empty – no page to give. driver shall allocate new page – supported from Kernel 4.9 | Acceleration |
| rx[i]_cache_busy | The number of events where cache head was busy and cannot be recycled. driver allocated new page – supported from Kernel 4.9 | Acceleration |
| rx[i]_xmit_more | The number of packets sent with xmit_more indication set on the skbuff (no doorbell) – Supported from kernel 4.8 | Acceleration |
| tx[i]_cqes | The number of completions received on the CQ of TX ring. Supported from kernel 4.19 | Informative |
| ch[i]_poll | The number of invocations of NAPI poll of channel. Supported from kernel 4.19 | Informative |
| ch[i]_arm | The number of times the NAPI poll function completed and armed the completion queues on channelSupported from kernel 4.19 | Informative |
| ch[i]_aff_change | The number of times the NAPI poll function explicitly stopped execution on a CPU due to a change in affinity, on channel. Supported from kernel 4.19 | Informative |
| rx[i]_congst_umr | The number of times an outstanding UMR request is delayed due to congestion, on ringSupported from kernel 4.19 | Error |
| ch[i]_events | The number of hard interrupt events on the completion queues of channel. Supported from kernel 4.19 | Informative |
| rx[i]_mpwqe_filler_strides | The number of strides consumed by filler CQEs on ring. Supported from kernel 4.19 | Informative |
| rx[i]_xdp_tx_xmit | The number of packets forwarded back to the port due to XDP program XDP_TX action (bouncing). these packets are not counted by other software counters. These packets are counted by physical port and vPort counters – supported from kernel 4.9Before kernel 4.19 name was rx[i]_xdp_tx | Informative |
| rx[i]_xdp_tx_full | The number of packets that should have been forwarded back to the port due to XDP_TX action but were dropped due to full tx queue. these packets are not counted by other software counters. These packets are counted by physical port and vPort countersyou may open more rx queues and spread traffic rx over all queues and/or increase rx ring sizesupported from kernel 4.9 | Error |
| rx[i]_xdp_tx_err | The number of times an XDP_TX error such as frame too long and frame too short occurred on XDP_TX ring of RX ring. Supported from kernel 4.19 | Error |
| rx[i]_xdp_tx_cqesrx_xdp_tx_cqe (1) | The number of completions received on the CQ of the XDP-TX ring. Supported from kernel 4.19 | Informative |
| rx[i]_xdp_drop | The number of packets dropped due to XDP program XDP_DROP action. these packets are not counted by other software counters. These packets are counted by physical port and vPort counters – supported from kernel 4.9 | Informative |
| rx[i]_xdp_redirect | The number of times an XDP redirect action was triggered on ring. .Supported from kernel 4.19 | Acceleration |
| tx[i]_xdp_xmit | The number of packets redirected to the interface(due to XDP redirect). These packets are not counted by other software counters. These packets are counted by physical port and vPort counters – Supported from kernel 4.19 | Informative |
| tx[i]_xdp_full | The number of packets redirected to the interface(due to XDP redirect), but were dropped due to full tx queue. these packets are not counted by other software counters. you may enlarge tx queues. Supported from kernel 4.19 | Informative |
| tx[i]_xdp_err | The number of packets redirected to the interface(due to XDP redirect) but were dropped due to error such as frame too long and frame too short . Supported from kernel 4.19 | Error |
| tx[i]_xdp_cqes | The number of completions received for packets redirected to the interface(due to XDP redirect) on the CQ . Supported from kernel 4.19 | Informative |
| rx[i]_cache_waive | The number of cache evacuation. This can occur due to page move to another NUMA node or page was pfmemalloc-ed and should be freed as soon as possible. Supported from kernel 4.14 | Acceleration |
Notes:
(1) The corresponding ring and global counters do not share the same name (i.e. do not follow the common naming scheme).
vPort Counters
Counters on the eswitch port that is connected to the VNIC.
vPort Counter Table
| Counter | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| rx_vport_unicast_packets | Unicast packets received, steered to a port including Raw Ethernet QP/DPDK traffic, excluding RDMA traffic | Informative |
| rx_vport_unicast_bytes | Unicast bytes received, steered to a port including Raw Ethernet QP/DPDK traffic, excluding RDMA traffic | Informative |
| tx_vport_unicast_packets | Unicast packets transmitted, steered from a port including Raw Ethernet QP/DPDK traffic, excluding RDMA traffic | Informative |
| tx_vport_unicast_bytes | Unicast bytes transmitted, steered from a port including Raw Ethernet QP/DPDK traffic, excluding RDMA traffic | Informative |
| rx_vport_multicast_packets | Multicast packets received, steered to a port including Raw Ethernet QP/DPDK traffic, excluding RDMA traffic | Informative |
| rx_vport_multicast_bytes | Multicast bytes received, steered to a port including Raw Ethernet QP/DPDK traffic, excluding RDMA traffic | Informative |
| tx_vport_multicast_packets | Multicast packets transmitted, steered from a port including Raw Ethernet QP/DPDK traffic, excluding RDMA traffic | Informative |
| tx_vport_multicast_bytes | Multicast bytes transmitted, steered from a port including Raw Ethernet QP/DPDK traffic, excluding RDMA traffic | Informative |
| rx_vport_broadcast_packets | Broadcast packets received, steered to a port including Raw Ethernet QP/DPDK traffic, excluding RDMA traffic | Informative |
| rx_vport_broadcast_bytes | Broadcast bytes received, steered to a port including Raw Ethernet QP/DPDK traffic, excluding RDMA traffic | Informative |
| tx_vport_broadcast_packets | Broadcast packets transmitted, steered from a port including Raw Ethernet QP/DPDK traffic, excluding RDMA traffic | Informative |
| tx_vport_broadcast_bytes | Broadcast packets transmitted, steered from a port including Raw Ethernet QP/DPDK traffic, excluding RDMA traffic | Informative |
| rx_vport_rdma_unicast_packets | RDMA unicast packets received, steered to a port (counters counts RoCE/UD/RC traffic) [A] | Acceleration |
| rx_vport_rdma_unicast_bytes | RDMA unicast bytes received, steered to a port (counters counts RoCE/UD/RC traffic) [A] | Acceleration |
| tx_vport_rdma_unicast_packets | RDMA unicast packets transmitted, steered from a port (counters counts RoCE/UD/RC traffic) [A] | Acceleration |
| tx_vport_rdma_unicast_bytes | RDMA unicast bytes transmitted, steered from a port (counters counts RoCE/UD/RC traffic) [A] | Acceleration |
| rx_vport_ rdma _multicast_packets | RDMA multicast packets received, steered to a port (counters counts RoCE/UD/RC traffic) [A] | Acceleration |
| rx_vport_ rdma _multicast_bytes | RDMA multicast bytes received, steered to a port (counters counts RoCE/UD/RC traffic) [A] | Acceleration |
| tx_vport_ rdma _multicast_packets | RDMA multicast packets transmitted, steered from a port (counters counts RoCE/UD/RC traffic) [A] | Acceleration |
| tx_vport_ rdma _multicast_bytes | RDMA multicast bytes transmitted, steered from a port (counters counts RoCE/UD/RC traffic) [A] | Acceleration |
| rx_steer_missed_packets | Number of packets that was received by the NIC, however was discarded because it did not match any flow in the NIC flow table. supported from kernel 4.16 | Error |
| rx_packets | Representor only: packets received, that were handled by the hypervisor. supported from kernel 4.18 | Informative |
| rx_bytes | Representor only: bytes received, that were handled by the hypervisor. supported from kernel 4.18 | Informative |
| tx_packets | Representor only: packets transmitted, that were handled by the hypervisor. supported from kernel 4.18 | Informative |
| tx_bytes | Representor only: bytes transmitted, that were handled by the hypervisor. supported from kernel 4.18 | Informative |
Physical Port Counters
The physical port counters are the counters on the external port connecting adapter to the network. This measuring point holds information on standardized counters like IEEE 802.3, RFC2863, RFC 2819, RFC 3635 and additional counters like flow control, FEC and more.
Physical Port Counter Table
| Counter | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| rx_packets_phy | The number of packets received on the physical port. This counter doesn’t include packets that were discarded due to FCS, frame size and similar errors.ConnectX-3 naming : rx_packets | Informative |
| tx_packets_phy | The number of packets transmitted on the physical port.ConnectX-3 naming : tx_packets | Informative |
| rx_bytes_phy | The number of bytes received on the physical port, including Ethernet header and FCS.ConnectX-3 naming : rx_bytes | Informative |
| tx_bytes_phy | The number of bytes transmitted on the physical port.ConnectX-3 naming : tx_bytes | Informative |
| rx_multicast_phy | The number of multicast packets received on the physical port.ConnectX-3 naming : rx_multicast_packets | Informative |
| tx_multicast_phy | The number of multicast packets transmitted on the physical port.ConnectX-3 naming : tx_multicast_packets | Informative |
| rx_broadcast_phy | The number of broadcast packets received on the physical port.ConnectX-3 naming : rx_broadcast_packets | Informative |
| tx_broadcast_phy | The number of broadcast packets transmitted on the physical port.ConnectX-3 naming : tx_broadcast_packets | Informative |
| rx_crc_errors_phy | The number of dropped received packets due to FCS (Frame Check Sequence) error on the physical port. If this counter is increased in high rate, check the link quality using rx_symbol_error_phy and rx_corrected_bits_phy counters below.ConnectX-3 naming : rx_crc_errors | Error |
| rx_in_range_len_errors_phy | The number of received packets dropped due to length/type errors on a physical port.ConnectX-3 naming : rx_in_range_length_error | Error |
| rx_out_of_range_len_phy | The number of received packets dropped due to length greater than allowed on a physical port.If this counter is increasing, it implies that the peer connected to the adapter has a larger MTU configured. Using same MTU configuration shall resolve this issue.ConnectX-3 naming : rx_out_range_length_error | Error |
| rx_oversize_pkts_phy | The number of dropped received packets due to length which exceed MTU size on a physical portIf this counter is increasing, it implies that the peer connected to the adapter has a larger MTU configured. Using same MTU configuration shall resolve this issue.ConnectX-3 naming : rx_frame_errors | Error |
| rx_symbol_err_phy | The number of received packets dropped due to physical coding errors (symbol errors) on a physical port. | Error |
| rx_mac_control_phy | The number of MAC control packets received on the physical port. | Informative |
| tx_mac_control_phy | The number of MAC control packets transmitted on the physical port. | Informative |
| rx_pause_ctrl_phy | The number of link layer pause packets received on a physical port. If this counter is increasing, it implies that the network is congested and cannot absorb the traffic coming from to the adapter. | Informative |
| tx_pause_ctrl_phy | The number of link layer pause packets transmitted on a physical port. If this counter is increasing, it implies that the NIC is congested and cannot absorb the traffic coming from the network. | Informative |
| rx_unsupported_op_phy | The number of MAC control packets received with unsupported opcode on a physical port. | Error |
| rx_discards_phy | The number of received packets dropped due to lack of buffers on a physical port. If this counter is increasing, it implies that the adapter is congested and cannot absorb the traffic coming from the network.ConnectX-3 naming : rx_fifo_errors | Error |
| tx_discards_phy | The number of packets which were discarded on transmission, even no errors were detected. the drop might occur due to link in down state, head of line drop, pause from the network, etc | Error |
| tx_errors_phy | The number of transmitted packets dropped due to a length which exceed MTU size on a physical port. | Error |
| rx_undersize_pkts_phy | The number of received packets dropped due to length which is shorter than 64 bytes on a physical port. If this counter is increasing, it implies that the peer connected to the adapter has a non-standard MTU configured or malformed packet had arrived. | Error |
| rx_fragments_phy | The number of received packets dropped due to a length which is shorter than 64 bytes and has FCS error on a physical port. If this counter is increasing, it implies that the peer connected to the adapter has a non-standard MTU configured. | Error |
| rx_jabbers_phy | The number of received packets d due to a length which is longer than 64 bytes and had FCS error on a physical port. | Error |
| rx_64_bytes_phy | The number of packets received on the physical port with size of 64 bytes. | Informative |
| rx_65_to_127_bytes_phy | The number of packets received on the physical port with size of 65 to 127 bytes. | Informative |
| rx_128_to_255_bytes_phy | The number of packets received on the physical port with size of 128 to 255 bytes. | Informative |
| rx_256_to_511_bytes_phy | The number of packets received on the physical port with size of 256 to 512 bytes. | Informative |
| rx_512_to_1023_bytes_phy | The number of packets received on the physical port with size of 512 to 1023 bytes. | Informative |
| rx_1024_to_1518_bytes_phy | The number of packets received on the physical port with size of 1024 to 1518 bytes. | Informative |
| rx_1519_to_2047_bytes_phy | The number of packets received on the physical port with size of 1519 to 2047 bytes. | Informative |
| rx_2048_to_4095_bytes_phy | The number of packets received on the physical port with size of 2048 to 4095 bytes. | Informative |
| rx_4096_to_8191_bytes_phy | The number of packets received on the physical port with size of 4096 to 8191 bytes. | Informative |
| rx_8192_to_10239_bytes_phy | The number of packets received on the physical port with size of 8192 to 10239 bytes. | Informative |
| link_down_events_phy | The number of times where the link operative state changed to down. In case this counter is increasing it may imply on port flapping. You may need to replace the cable/transceiver. | Error |
| rx_out_of_buffer | Number of times receive queue had no software buffers allocated for the adapter’s incoming traffic. | Error |
| module_bus_stuck | The number of times that module’s I2C bus (data or clock) short-wire was detected. You may need to replace the cable/transceiver – supported from kernel 4.10 | Error |
| module_high_temp | The number of times that the module temperature was too high. If this issue persist, you may need to check the ambient temperature or replace the cable/transceiver module – supported from kernel 4.10 | Error |
| module_bad_shorted | The number of times that the module cables were shorted. You may need to replace the cable/transceiver module – supported from kernel 4.10 | Error |
| module_unplug | The number of times that module was ejected – supported from kernel 4.10 | Informative |
| rx_buffer_passed_thres_phy | The number of events where the port receive buffer was over 85% full. Supported from kernel 4.14 | Informative |
| tx_pause_storm_warning_events | The number of times the device was sending pauses for a long period of time – supported from kernel 4.15 | Informative |
| tx_pause_storm_error_events | The number of times the device was sending pauses for a long period of time, reaching time out and disabling transmission of pause frames. on the period where pause frames were disabled, drop could have been occurred – supported from kernel 4.15 | Error |
| rx[i]_buff_alloc_err / rx_buff_alloc_err | Failed to allocate a buffer to received packet (or SKB) on port (or per ring) | Error |
| rx_bits_phy | This counter provides information on the total amount of traffic that could have been received and can be used as a guideline to measure the ratio of errored traffic in rx_pcs_symbol_err_phy& rx_corrected_bits_phy. | Informative |
| rx_pcs_symbol_err_phy | This counter counts the number of symbol errors that wasn’t corrected by FEC correction algorithm or that FEC algorithm was not active on this interface. If this counter is increasing, it implies that the link between the NIC and the network is suffering from high BER, and that traffic is lost. You may need to replace the cable/transceiver. The error rate is the number of rx_pcs_symbol_err_phy divided by the number of rx_phy_bits on a specific time frame. | Error |
| rx_corrected_bits_phy | The number of corrected bits on this port according to active FEC (RS/FC). If this counter is increasing, it implies that the link between the NIC and the network is suffering from high BER. The corrected bit rate is the number of rx_corrected_bits_phy divided by the number of rx_phy_bits on a specific time frame | Error |
| phy_raw_errors_lane[l] | This counter counts the number of physical raw errors per lane [l] index. The counter counts errors before FEC corrections. If this counter is increasing, it implies that the link between the NIC and the network is suffering from high BER, and that traffic might be lost. You may need to replace the cable/transceiver. Please check in accordance with rx_corrected_bits_phy. Supported from kernel 4.20 | Error |
Priority Port Counters
The following counters are physical port counters that being counted per L2 priority (0-7).
Note: ‘p’ in the counter name represents the priority.
Priority Port Counter Table
| Counter | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| rx_prio[p]_bytes | The number of bytes received with priority p on the physical port.ConnectX-3 naming :rx_prio_[p]_bytes. this counter also counts packets with no vlan | Informative |
| rx_prio[p]_packets | The number of packets received with priority p on the physical port.ConnectX-3 naming : rx_prio_[p]_packets. this counter also counts packets with no vlan | Informative |
| tx_prio[p]_bytes | The number of bytes transmitted on priority p on the physical port.ConnectX-3 naming :tx_prio_[p]_bytes. | Informative |
| tx_prio[p]_packets | The number of packets transmitted on priority p on the physical port.ConnectX-3 naming : tx_prio_[p]_packets. | Informative |
| rx_prio[p]_pause | The number of pause packets received with priority p on a physical port. If this counter is increasing, it implies that the network is congested and cannot absorb the traffic coming from the adapter.Note: This counter is available only if PFC was enabled on priority p. Refer to HowTo Configure PFC on ConnectX-4 .ConnectX-3 naming : rx_pause_prio_p | Informative |
| rx_prio[p]_pause_duration | The duration of pause received (in microSec) on priority p on the physical port. The counter represents the time the port did not send any traffic on this priority. If this counter is increasing, it implies that the network is congested and cannot absorb the traffic coming from the adapter.Note: This counter is available only if PFC was enabled on priority p. Refer to HowTo Configure PFC on ConnectX-4 .ConnectX-3 naming : rx_pause_duration_prio_p | Informative |
| rx_prio[p]_pause_transition | The number of times a transition from Xoff to Xon on priority p on the physical port has occurred.Note: This counter is available only if PFC was enabled on priority p. Refer to HowTo Configure PFC on ConnectX-4 .ConnectX-3 naming : rx_pause_transition_prio_p | Informative |
| tx_prio[p]_pause | The number of pause packets transmitted on priority p on a physical port. If this counter is increasing, it implies that the adapter is congested and cannot absorb the traffic coming from the network.Note: This counter is available only if PFC was enabled on priority p. Refer to HowTo Configure PFC on ConnectX-4 .ConnectX-3 naming : tx_pause_prio_p | Informative |
| tx_prio[p]_pause_duration | The duration of pause transmitter (in microSec) on priority p on the physical port.Note: This counter is available only if PFC was enabled on priority p. Refer to HowTo Configure PFC on ConnectX-4 .ConnectX-3 naming : tx_pause_duration_prio_p | Informative |
| rx_prio[p]_buf_discard | The number of packets discarded by device due to lack of per host receive buffers. Supported from kernel 5.3 | Informative |
| rx_prio[p]_cong_discard | The number of packets discarded by device due to per host congestion. Supported from kernel 5.3 | Informative |
| rx_prio[p]_marked | The number of packets ecn marked by device due to per host congestion. Supported from kernel 5.3 | Informative |
| rx_prio[p]_discard | The number of packets discarded by device due to lack of receive buffers. Supported from kernel 5.6 | Infornative |
Device Counters
| Counter | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| rx_pci_signal_integrity | Counts physical layer PCIe signal integrity errors, the number of transitions to recovery due to Framing errors and CRC (dlp and tlp).If this counter is raising, try moving the adapter card to a different slot to rule out a bad PCI slot. Validate that you are running with the latest firmware available and latest server BIOS version. | Error |
| tx_pci_signal_integrity | Counts physical layer PCIe signal integrity errors, the number of transition to recovery initiated by the other side (moving to recovery due to getting TS/EIEOS).If this counter is raising, try moving the adapter card to a different slot to rule out a bad PCI slot. Validate that you are running with the latest firmware available and latest server BIOS version. | Error |
| outbound_pci_buffer_overflow | The number of packets dropped due to pci buffer overflow. If this counter is raising in high rate, it might indicate that the receive traffic rate for a host is larger than the PCIe bus and therefore a congestion occurs. Supported from kernel 4.14 | Informative |
| outbound_pci_stalled_rd | The percentage (in the range 0…100) of time within the last second that the NIC had outbound non-posted reads requests but could not perform the operation due to insufficient posted credits. Supported from kernel 4.14 | Informative |
| outbound_pci_stalled_wr | The percentage (in the range 0…100) of time within the last second that the NIC had outbound posted writes requests but could not perform the operation due to insufficient posted credits. Supported from kernel 4.14 | Informative |
| outbound_pci_stalled_rd_events | The number of seconds where outbound_pci_stalled_rd was above 30%. Supported from kernel 4.14 | Informative |
| outbound_pci_stalled_wr_events | The number of seconds where outbound_pci_stalled_wr was above 30%. Supported from kernel 4.14 | Informative |
| dev_out_of_buffer | The number of times the device owned queue had not enough buffers allocated | Error |
Full List of Counters
# ethtool -S eth5
NIC statistics:
rx_packets: 10
rx_bytes: 3420
tx_packets: 18
tx_bytes: 1296
tx_tso_packets: 0
tx_tso_bytes: 0
tx_tso_inner_packets: 0
tx_tso_inner_bytes: 0
tx_added_vlan_packets: 0
tx_nop: 0
rx_lro_packets: 0
rx_lro_bytes: 0
rx_ecn_mark: 0
rx_removed_vlan_packets: 0
rx_csum_unnecessary: 0
rx_csum_none: 0
rx_csum_complete: 10
rx_csum_unnecessary_inner: 0
rx_xdp_drop: 0
rx_xdp_redirect: 0
rx_xdp_tx_xmit: 0
rx_xdp_tx_full: 0
rx_xdp_tx_err: 0
rx_xdp_tx_cqe: 0
tx_csum_none: 18
tx_csum_partial: 0
tx_csum_partial_inner: 0
tx_queue_stopped: 0
tx_queue_dropped: 0
tx_xmit_more: 0
tx_recover: 0
tx_cqes: 18
tx_queue_wake: 0
tx_udp_seg_rem: 0
tx_cqe_err: 0
tx_xdp_xmit: 0
tx_xdp_full: 0
tx_xdp_err: 0
tx_xdp_cqes: 0
rx_wqe_err: 0
rx_mpwqe_filler_cqes: 0
rx_mpwqe_filler_strides: 0
rx_buff_alloc_err: 0
rx_cqe_compress_blks: 0
rx_cqe_compress_pkts: 0
rx_page_reuse: 0
rx_cache_reuse: 0
rx_cache_full: 0
rx_cache_empty: 2688
rx_cache_busy: 0
rx_cache_waive: 0
rx_congst_umr: 0
rx_arfs_err: 0
ch_events: 75
ch_poll: 75
ch_arm: 75
ch_aff_change: 0
ch_eq_rearm: 0
rx_out_of_buffer: 0
rx_if_down_packets: 15
rx_steer_missed_packets: 0
rx_vport_unicast_packets: 0
rx_vport_unicast_bytes: 0
tx_vport_unicast_packets: 0
tx_vport_unicast_bytes: 0
rx_vport_multicast_packets: 2
rx_vport_multicast_bytes: 172
tx_vport_multicast_packets: 12
tx_vport_multicast_bytes: 936
rx_vport_broadcast_packets: 37
rx_vport_broadcast_bytes: 9270
tx_vport_broadcast_packets: 6
tx_vport_broadcast_bytes: 360
rx_vport_rdma_unicast_packets: 0
rx_vport_rdma_unicast_bytes: 0
tx_vport_rdma_unicast_packets: 0
tx_vport_rdma_unicast_bytes: 0
rx_vport_rdma_multicast_packets: 0
rx_vport_rdma_multicast_bytes: 0
tx_vport_rdma_multicast_packets: 0
tx_vport_rdma_multicast_bytes: 0
tx_packets_phy: 0
rx_packets_phy: 0
rx_crc_errors_phy: 0
tx_bytes_phy: 0
rx_bytes_phy: 0
tx_multicast_phy: 0
tx_broadcast_phy: 0
rx_multicast_phy: 0
rx_broadcast_phy: 0
rx_in_range_len_errors_phy: 0
rx_out_of_range_len_phy: 0
rx_oversize_pkts_phy: 0
rx_symbol_err_phy: 0
tx_mac_control_phy: 0
rx_mac_control_phy: 0
rx_unsupported_op_phy: 0
rx_pause_ctrl_phy: 0
tx_pause_ctrl_phy: 0
rx_discards_phy: 0
tx_discards_phy: 0
tx_errors_phy: 0
rx_undersize_pkts_phy: 0
rx_fragments_phy: 0
rx_jabbers_phy: 0
rx_64_bytes_phy: 0
rx_65_to_127_bytes_phy: 0
rx_128_to_255_bytes_phy: 0
rx_256_to_511_bytes_phy: 0
rx_512_to_1023_bytes_phy: 0
rx_1024_to_1518_bytes_phy: 0
rx_1519_to_2047_bytes_phy: 0
rx_2048_to_4095_bytes_phy: 0
rx_4096_to_8191_bytes_phy: 0
rx_8192_to_10239_bytes_phy: 0
link_down_events_phy: 0
rx_prio0_bytes: 0
rx_prio0_packets: 0
tx_prio0_bytes: 0
tx_prio0_packets: 0
rx_prio1_bytes: 0
rx_prio1_packets: 0
tx_prio1_bytes: 0
tx_prio1_packets: 0
rx_prio2_bytes: 0
rx_prio2_packets: 0
tx_prio2_bytes: 0
tx_prio2_packets: 0
rx_prio3_bytes: 0
rx_prio3_packets: 0
tx_prio3_bytes: 0
tx_prio3_packets: 0
rx_prio4_bytes: 0
rx_prio4_packets: 0
tx_prio4_bytes: 0
tx_prio4_packets: 0
rx_prio5_bytes: 0
rx_prio5_packets: 0
tx_prio5_bytes: 0
tx_prio5_packets: 0
rx_prio6_bytes: 0
rx_prio6_packets: 0
tx_prio6_bytes: 0
tx_prio6_packets: 0
rx_prio7_bytes: 0
rx_prio7_packets: 0
tx_prio7_bytes: 0
tx_prio7_packets: 0
module_unplug: 0
module_bus_stuck: 0
module_high_temp: 0
module_bad_shorted: 0
ch0_events: 9
ch0_poll: 9
ch0_arm: 9
ch0_aff_change: 0
ch0_eq_rearm: 0
ch1_events: 23
ch1_poll: 23
ch1_arm: 23
ch1_aff_change: 0
ch1_eq_rearm: 0
ch2_events: 8
ch2_poll: 8
ch2_arm: 8
ch2_aff_change: 0
ch2_eq_rearm: 0
ch3_events: 19
ch3_poll: 19
ch3_arm: 19
ch3_aff_change: 0
ch3_eq_rearm: 0
ch4_events: 8
ch4_poll: 8
ch4_arm: 8
ch4_aff_change: 0
ch4_eq_rearm: 0
ch5_events: 8
ch5_poll: 8
ch5_arm: 8
ch5_aff_change: 0
ch5_eq_rearm: 0
rx0_packets: 0
rx0_bytes: 0
rx0_csum_complete: 0
rx0_csum_unnecessary: 0
rx0_csum_unnecessary_inner: 0
rx0_csum_none: 0
rx0_xdp_drop: 0
rx0_xdp_redirect: 0
rx0_lro_packets: 0
rx0_lro_bytes: 0
rx0_ecn_mark: 0
rx0_removed_vlan_packets: 0
rx0_wqe_err: 0
rx0_mpwqe_filler_cqes: 0
rx0_mpwqe_filler_strides: 0
rx0_buff_alloc_err: 0
rx0_cqe_compress_blks: 0
rx0_cqe_compress_pkts: 0
rx0_page_reuse: 0
rx0_cache_reuse: 0
rx0_cache_full: 0
rx0_cache_empty: 448
rx0_cache_busy: 0
rx0_cache_waive: 0
rx0_congst_umr: 0
rx0_arfs_err: 0
rx0_xdp_tx_xmit: 0
rx0_xdp_tx_full: 0
rx0_xdp_tx_err: 0
rx0_xdp_tx_cqes: 0
rx1_packets: 10
rx1_bytes: 3420
rx1_csum_complete: 10
rx1_csum_unnecessary: 0
rx1_csum_unnecessary_inner: 0
rx1_csum_none: 0
rx1_xdp_drop: 0
rx1_xdp_redirect: 0
rx1_lro_packets: 0
rx1_lro_bytes: 0
rx1_ecn_mark: 0
rx1_removed_vlan_packets: 0
rx1_wqe_err: 0
rx1_mpwqe_filler_cqes: 0
rx1_mpwqe_filler_strides: 0
rx1_buff_alloc_err: 0
rx1_cqe_compress_blks: 0
rx1_cqe_compress_pkts: 0
rx1_page_reuse: 0
rx1_cache_reuse: 0
rx1_cache_full: 0
rx1_cache_empty: 448
rx1_cache_busy: 0
rx1_cache_waive: 0
rx1_congst_umr: 0
rx1_arfs_err: 0
rx1_xdp_tx_xmit: 0
rx1_xdp_tx_full: 0
rx1_xdp_tx_err: 0
rx1_xdp_tx_cqes: 0
rx2_packets: 0
rx2_bytes: 0
rx2_csum_complete: 0
rx2_csum_unnecessary: 0
rx2_csum_unnecessary_inner: 0
rx2_csum_none: 0
rx2_xdp_drop: 0
rx2_xdp_redirect: 0
rx2_lro_packets: 0
rx2_lro_bytes: 0
rx2_ecn_mark: 0
rx2_removed_vlan_packets: 0
rx2_wqe_err: 0
rx2_mpwqe_filler_cqes: 0
rx2_mpwqe_filler_strides: 0
rx2_buff_alloc_err: 0
rx2_cqe_compress_blks: 0
rx2_cqe_compress_pkts: 0
rx2_page_reuse: 0
rx2_cache_reuse: 0
rx2_cache_full: 0
rx2_cache_empty: 448
rx2_cache_busy: 0
rx2_cache_waive: 0
rx2_congst_umr: 0
rx2_arfs_err: 0
rx2_xdp_tx_xmit: 0
rx2_xdp_tx_full: 0
rx2_xdp_tx_err: 0
rx2_xdp_tx_cqes: 0
…
tx0_packets: 1
tx0_bytes: 60
tx0_tso_packets: 0
tx0_tso_bytes: 0
tx0_tso_inner_packets: 0
tx0_tso_inner_bytes: 0
tx0_csum_partial: 0
tx0_csum_partial_inner: 0
tx0_added_vlan_packets: 0
tx0_nop: 0
tx0_csum_none: 1
tx0_stopped: 0
tx0_dropped: 0
tx0_xmit_more: 0
tx0_recover: 0
tx0_cqes: 1
tx0_wake: 0
tx0_cqe_err: 0
tx1_packets: 5
tx1_bytes: 300
tx1_tso_packets: 0
tx1_tso_bytes: 0
tx1_tso_inner_packets: 0
tx1_tso_inner_bytes: 0
tx1_csum_partial: 0
tx1_csum_partial_inner: 0
tx1_added_vlan_packets: 0
tx1_nop: 0
tx1_csum_none: 5
tx1_stopped: 0
tx1_dropped: 0
tx1_xmit_more: 0
tx1_recover: 0
tx1_cqes: 5
tx1_wake: 0
tx1_cqe_err: 0
tx2_packets: 0
tx2_bytes: 0
tx2_tso_packets: 0
tx2_tso_bytes: 0
tx2_tso_inner_packets: 0
tx2_tso_inner_bytes: 0
tx2_csum_partial: 0
tx2_csum_partial_inner: 0
tx2_added_vlan_packets: 0
tx2_nop: 0
tx2_csum_none: 0
tx2_stopped: 0
tx2_dropped: 0
tx2_xmit_more: 0
tx2_recover: 0
tx2_cqes: 0
tx2_wake: 0
tx2_cqe_err: 0
…
The number of packets dropped due to XDP program XDP_DROP action. these packets are not counted by other software counters. These packets are counted by physical port and vPort counters – supported from kernel 4.9



加油,兄弟
一起加油